Statement of changes in equity
Because all relevant information can be obtained from the balance sheet, this equation is known as a balance sheet equation. This represents the balance of shareholders’ equity reserves at the end of the reporting period as reflected in the statement of financial position. The statement of equity is the part of a balance sheet or ledger that calculates and explains the shareholders’ equity. The cost of equity is another vital measure to evaluate when analyzing a shareholders equity statement. It represents the return investors require for investing their equity in the firm. If an organization’s return on equity is below its cost of equity, this indicates that it’s not rewarding its shareholders adequately for the risk they bear to invest their funds in the company.

On the other hand, the borrowing of $60,000 had a favorable or positive effect on the corporation’s cash balance. The net result of the four financing activities caused cash and cash equivalents to increase by $28,000. If accounts payable decreased by $9,000 the corporation must have paid more than the amount of expenses that were included in the income statement. Paying more than the amount in the income statement is unfavorable for the corporation’s cash balance. As a result the $9,000 decrease in accounts payable will appear in parentheses on the SCF. In the United States, the statement of changes in equity is also called the statement of retained earnings.
Importance of Shareholders Equity Statement
An alternative calculation of company equity is the value of share capital and retained earnings less the value of treasury shares. Treasury shares continue to count as issued shares, but they are not considered to be statement of stockholders equity outstanding and are thus not included in dividends or the calculation of earnings per share (EPS). Treasury shares can always be reissued back to stockholders for purchase when companies need to raise more capital.
- A company’s profit that is not distributed as dividends is known as retained earnings, which are another important contributor to shareholders equity.
- Stockholders’ equity might include common stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and treasury stock.
- This is especially true when dealing with companies that have been in business for many years.
- The balance sheet shows this decrease is due to a decrease in assets, but a larger decrease in liabilities.
- The shareholders equity statement acts as a bridge between the company and its shareholders, providing them vital information about the company’s financial health and operations.
- He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
The following examples illustrate journal entries that can cause stockholders’ equity to change. Moreover, if such initiatives do not yield anticipated financial returns, they could lead to a decline in total shareholders’ equity. Such a scenario may create tension with shareholders, particularly those that primarily focus on financial returns. On the other hand, using shareholders’ equity for CSR and sustainability initiatives could involve certain challenges.
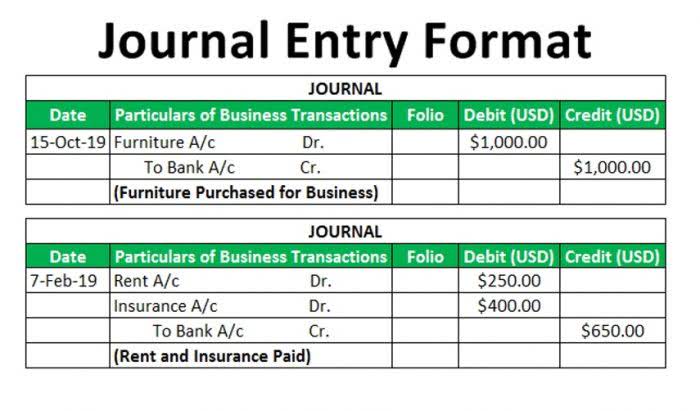
Example statement
Regular monitoring of these adjustments not only helps gauge fiscal health but also in strategic future planning. If equity continually expands over time, it’s a positive sign of growth, implying good management and a healthy financial status. In the United States this is called a statement of retained earnings and it is required under the U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (U.S. GAAP) whenever comparative balance sheets and income statements are presented. It may appear in the balance sheet, in a combined income statement and changes in retained earnings statement, or as a separate schedule. The statement’s heading should include the company name, the title of the statement and the accounting period to prevent confusion when you search for these financial statements later.
- However, examining these changes on a quarterly basis might give more immediate insights into the company’s performance and any recent events impacting its equity.
- Second all dividends and net losses are subtracted from the equity balance giving you the ending equity balance for the accounting period.
- Long-term liabilities are obligations that are due for repayment in periods longer than one year, such as bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations.
- It’s crucial to dig deeper and combine these insights with additional financial statement analysis for a more comprehensive picture.
- The statement, which reveals changes in equity over a specified period, gives stakeholders a clear look at how equity is being managed.
Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching. After almost a decade of experience in public accounting, he created MyAccountingCourse.com to help https://www.bookstime.com/ people learn accounting & finance, pass the CPA exam, and start their career. This is because years of retained earnings could be used for expenses or any asset to help the business grow.
What Is Stockholders’ Equity?
This reverse capital exchange between a company and its stockholders is known as share buybacks. Shares bought back by companies become treasury shares, and their dollar value is noted in the treasury stock contra account. In a balance sheet, shareholder’s equity is the discrepancy between the total assets and total liabilities.



